Question: Should I Remove the Laptop Battery For A Desktop Replacement Laptop?
I have a laptop at home which I use as a desktop replacement. As such, 99% of the time the laptop is being used it is plugged in. I wonder if I should remove the battery so that it is not permanently being charged, or does the laptop cut off the current to the battery once it is fully charged? I do unplug the laptop when I turn it off.
Answer:
No, you don’t need to care about battery when using a laptop as a desktop replacement, the laptop don’t charge battery all the time, the battery only be charge in the condition when battery level is lower than 95% (or other level).
It is out of date that some articles said ” Remove the battery – making sure that it is charged to 40% and store it in a dry, warm place. Ensure that it is wrapped protectively and nothing will be dropped on it “.
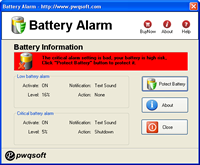
No cateBattery Alarm – Protect Laptop Battery
Battery Alarm is battery protection solution for windows laptop, it is designed to protect laptop battery from deep-discharge, the laptop battery may last for 3 years or more after using this software.
the windows default power alarm setting is not good, it may cause battery deep-discharge, the battery can be permantently damage and lifetime greatly reduced. Battery Alarm change windows power management scheme to prevent battery been discharged deeply.
Everybody can use this software to protect your laptop battery now !
 |
 |
Key feature
- One-Click to protect battery.
- Protect battery which will be able to use for 3 years or more.
- No extra hardware needed.
- Support Windows2000/2003/XP/Vista/2008/7.
Screenshots
 |
 |
 |
 |
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the newest technology batteries and offer several advantages over NiMH and NiCd batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are preferred for their lighter weight and higher performance. Lithium-ion batteries are typically 20-35% lighter and will provide 10-20% better performance than a NiMH battery of equivalent mAh rating.
Lithium-ion batteries are also unique in that they are not susceptible to the “memory effect”. A new Lithium-ion battery will benefit from an initial “conditioning” of the battery. For the first 3 charge cycles, fully charge the battery overnight before recharging. Once conditioned, Lithium-ion batteries will perform best when charged at a rate somewhere between a conventional slow charge and a rapid charge. When rapid charging, Lithium-ion batteries require a charger designed to charge Lithium batteries.
To achieve a true full charge when rapid charging, the battery needs to be slow charged the last 10-15% of its charge cycle. Most “intelligent” desktop and Lithium-battery rapid chargers provide this capability. A Lithium-ion battery may be damaged by extensive overcharging (continuously on a charger for more than 24 hours).
No cateOther Product
Protect Laptop Battery

Google Calendar Desktop